Fabric Scanners and Digital Materials Are Driving Sustainable Fashion Design
The fashion industry is entering a new era where innovation and sustainability are key for long-term success. With the industry responsible for 20% of global wastewater and generating 92 million tonnes of textile waste annually, the need for sustainable alternatives is more urgent than ever.
Emerging technologies like generative AI, virtual reality, and augmented reality present transformative opportunities. These advancements can lead to more efficient production processes and significantly reduce environmental impact. Digital materials, in particular, offer a promising solution to the industry’s waste challenges by enabling a digital-first approach to product design and creation.
As digital materials become central to sustainable practices, many businesses are seeking material digitization solutions. Designers and manufacturers are increasingly converting physical textiles into digital assets, a process driven by the growing adoption of digital product creation (DPC) workflows. Designers benefit from the flexibility of digital materials. They can experiment with patterns, colors, and textures digitally before ordering physical samples. Turing to 3D digital design can open new creative opportunities and new ways of working.
Digital materials also allow brands to explore “phygital” (physical and digital) experiences, offering new customer engagement methods. For instance, Gucci generated over $1 million by selling 100,000 digital items in the metaverse, illustrating the commercial potential of digital fashion. Digital assets can unlock new revenue streams and customer engagement strategies.
According to the Interline DPC Report 2023, DPC is reshaping the fashion industry by enabling more efficient, sustainable, and creative workflows through 3D technologies. This shift is a necessary evolution as brands seek to balance creativity with environmental responsibility.
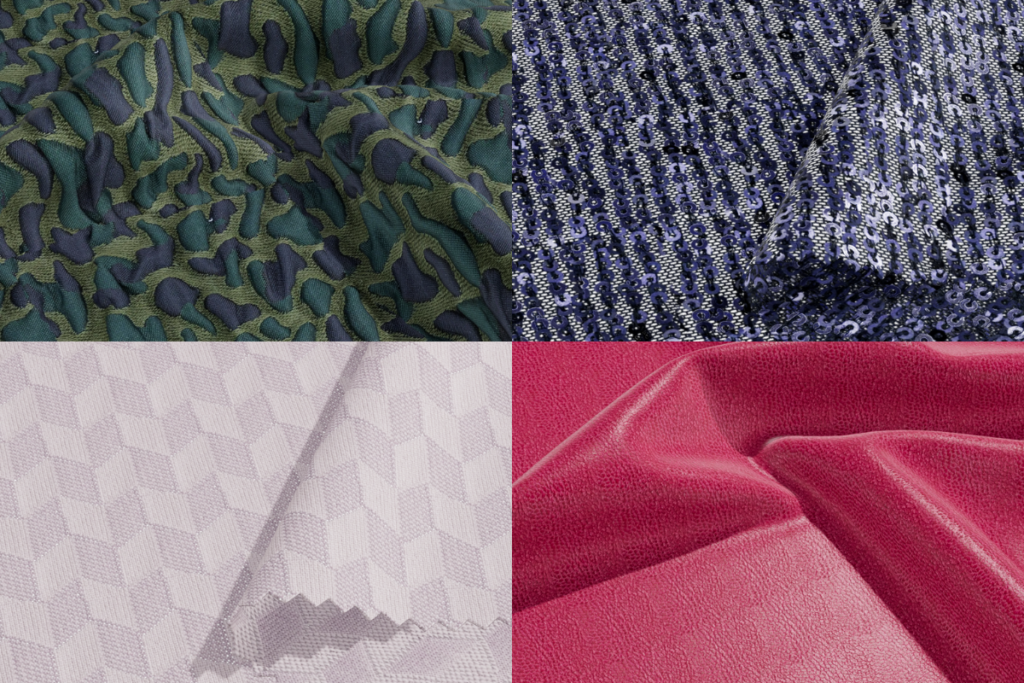

What Is A Fabric Scanner?
There are many methods to digitize physical materials. A popular option is flatbed scanners that capture the physical details of materials, including texture, pattern, color, and type. These scanners are one of the primary tools for creating high-quality digital representations, or “digital twins,” of materials. These digital “twins” replicating physical fabrics allow for rapid iterations and optimizations of product designs. Adjustments can be made in real time, reducing cumbersome physical tests and fabric sample cycles before a design goes to production.
Fabric scanners create comprehensive texture maps that allow computers to visualize the material in 3D. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and uniform lighting, scanners eliminate shadows and glare to ensure accurate color representation.
Importance Of Fabric Scanners In 2024
The demand for fabric scanners continues to grow as textile-related industries, including apparel, footwear, and home furnishings, increasingly adopt digital workflows. Fabric scanners bridge the gap between physical textiles and digital designs and help build a digital asset library for future use.
Fabric scanners significantly reduce the need for physical samples by allowing designers to visualize fabric properties in 3D. This enables them to experiment with different colors, textures, and patterns before committing to samples or prototypes. Digital design offers a flexible and fast way to respond quickly to what’s trending.
These scanners also support sustainable initiatives. Fewer sampling rounds mean less transportation costs and carbon footprint. This alignment with global sustainability goals makes fabric scanners key in creating more efficient, innovative, and eco-friendly production workflows.
7 Considerations When Looking For A Fabric Scanner
Clarify your selection criteria before investing in the right fabric scanner for your digital needs.
Here are 7 key factors to keep in mind:
1. Texture Map Output
Texture maps contain details of a fabric’s surface to create realistic 3D renderings. They play a pivotal role in PBR (Physically Based Rendering) by simulating how light interacts with materials in a digital environment. PBR relies on high-resolution texture maps to ensure every nuance of the fabric, from weave to sheen, is accurately represented.
Tip: Before making a purchase, ask for sample scans to evaluate the quality of texture map outputs. Assess how well the scanner captures the details of your specific materials.
2. Tiling & Editing Features
Seamless tiling is essential for creating large digital swatches. Most scanners come with software offering post-scan editing tools.
Key features to look for include:
- Tiling and cropping: check how quickly it can help you create seamless tiles
- Color adjustments: confirm color matching and adjustment capabilities
- Texture map export: ensure the file format and map quality are what you need
- PBR texture modifications: fine-tune your material’s appearance.
Choose a scanner with robust editing features that suit your workflow. The right software can significantly enhance the value of your scans, providing more flexibility and control over the final output.
3. Scan Resolution and Image Quality
Scan quality depends on DPI (dots per inch), with higher DPI settings capturing finer details. Fabric scans range from 300 to 1,200 DPI. Higher DPI (~600-1200) offers sharper detail but results in larger files, which require more storage and processing power. Lower DPI (~300-600) balances between detail and file size, ideal for collaborative work.
DPI output varies depending on the type of technology used to capture images. 3D flatbed fabric scanners commonly use smartphones or DSLR campers.
Select a DPI range that aligns with your specific needs, whether for quick sharing or detailed final production. Find the balance between image quality and file manageability without overwhelming your systems.
4. Customer Service
Reliable customer support and a good warranty can save you a lot of headaches down the line. Responsive service can help you resolve issues quickly and provide guidance on using the scanner effectively.
Check the customer support options, warranty options, and availability of training resources before purchasing. Having access to a knowledgeable support team and comprehensive training can significantly enhance your experience with the scanner.
5. Ease of Use
A user-friendly scanner with an intuitive interface is essential for seamless integration into your workflow. Look for features that streamline your process, such as batch scanning or straightforward file management. The ease of use can often be a deciding factor, especially in environments where multiple team members will use the scanner.
Consider how easily the scanner can be set up and operated with minimal training. Inquire about training or any tutorials that can help with onboarding.
6. Pricing
Scanner pricing varies widely depending on the features you’re looking for. Some offer hardware and software bundles while others sell them separately.
More expensive scanners typically include advanced features and greater customization capabilities, making them ideal for larger enterprises with specific needs. However, budget-friendly options are available for small businesses or individual designers who need reliable scanning without breaking the bank.
When evaluating pricing, look for transparency. Clarify what’s included in the purchase, such as software updates, maintenance, and customer support, to avoid potential hidden costs.
7. Software Integration
Chances are you’ll already be using a 3D design tool or software. The key to a successful scanner integration is making sure it fits into your existing software.
Verify compatibility with popular tools like CLO3D, Browzwear, and Adobe Suite. Check if the scanner supports multiple file formats, such as .U3M or .JPEG.
Proper integration means incorporating digital fabrics into your existing processes without needing to overhaul your workflow.
Top 3 Fabric Scanners 2024
NunoX Premium Scanner

NunoX, based in Taiwan, specializes in integrating AI with 3D scanning technology to create high-quality digital twins of materials. The NunoX Premium Scanner, combined with its cloud-based software, simplifies the process of material digitization through advanced AI features. This asynchronous workflow supports batch scanning and separate tile editing, providing flexibility and efficiency.
NunoX products are designed to streamline the entire digital textile workflow from scanning to editing. Users can easily visualize and manipulate digital materials without needing physical samples. The NunoX Cloud platform is accessible via popular web browsers, facilitating global collaboration. Key AI-powered features include texture map generation, automatic tiling, and fabric physics simulation.
Products:
- NunoX Premium Scanner: High-resolution material capture using the Canon EOS R5 camera.
- NunoX Cloud: Cloud-based material editor with AI capabilities
- AI texture map generation from image
- AI fabric tiling
- AI fabric physics
- Color change
- HD image gallery
- PBR texture maps
Vizoo xTex Scanner

Founded in 2013 and based in Germany, Vizoo focuses on high-resolution 3D scanning and texture creation. The company’s flagship product, the xTex Scanner, captures detailed digital representations of fabrics, allowing designers and manufacturers to work with highly accurate digital versions of physical materials.
The xTex Scanner is complemented by the xTex Software, which enables users to edit and manage scanned materials efficiently. The software supports a wide range of file formats and is compatible with industry-standard 3D design tools like CLO3D and Browzwear.
Products:
- xTex Scanner: High-resolution material capture using Nikon’s D850 and Z7 camera series.
- xTex Software: Material editor
- Texture tiling
- Digital color dyeing
- HD image generation
- PBR texture maps
- PhysX Platform: Database providing physical parameters for 3D garment simulation
DMix SampIR Scanner

The DMIx SamplR scanner, developed by ColorDigital GmbH in Germany, uses iPhone camera technology to capture videos and images of the material to create digital twins. DMix offers a robust digital ecosystem that combines color management, 3D technology, and material digitization, making it a versatile tool for designers and manufacturers.
The DMix system includes a comprehensive color library and spectral color analysis to ensure consistent color precision across all digital materials. Dmix allows designers, manufacturers, and brands to visualize materials with high accuracy before committing to physical samples.
Products:
- DMix SampIR: High-quality material capture tool using the iPhone 15 camera.
- DMix platform: Cloud-based material editor
- 3D-Magic tool for tiling and color appearance changes
- Remote texture development
- PBR texture maps
Fabric Scanner Comparison Summary Table
| NunoX | Vizoo | DMIx | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Hardware | NunoX Premium Scanner | xTex Scanner Hardware | SampIR |
| Software | NunoX Cloud | xTex Software | DMix Platform |
| Scan Area | A4 30 x 20 cm | A4, A2 | ~A4 30 x 22.5 cm |
| Resolution | 700 dpi | A4: 630 – 950 dpi A2: 340 – 720 dpi | 330 dpi |
| Capture Time | 30 seconds | 1-3 minutes | – |
| Capture Technology (Camera) | Canon EOS R5 | Nikon D850, Nikon Z7 series 45megapixels | iPhone 15 / 15 Plus |
| Scanner Device Control | NunoX App | xTex™ Production Software | App |
| Hardware Size | 60 x 60x 50 cm (23.6 x 23.6 x 19.7 in) | A4: 48 x 58 x 36 cm (18.9 x 22.8 x 14.2 in) A2: 92.5 x 93.3 x 166.3 cm (36.4 x 36.7 x 65.5 in) | 50 x 50 x 25 cm |
| PBR Texture Maps & Manipulation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| File Output Formats | U3M, U3MA, JPG, PNG | U3M, U3MA, xTex, SBS, SBSAR, MDL, JPG, PNG, TIFF (8, 16 bit) | GLTF, PNG |
| Compatibility | Browzwear CLO3D Other APIs | Browzwear CLO3D Other APIs | CLO3D Adobe Substance Other APIs |
| Specialization | AI tools | – | Color management |
| Software Compatibility | Mac OS Microsoft Windows | Microsoft Windows | Mac OS Microsoft Windows |
| Tiling tools | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PBR Texture Maps | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3D Renderings & material view | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Video capture | X | X | 4K / 60 FPS |
Why Go Digital?
As industries evolve and the demand for efficiency and sustainability grows, transitioning to digital materials has become more than just a trend.
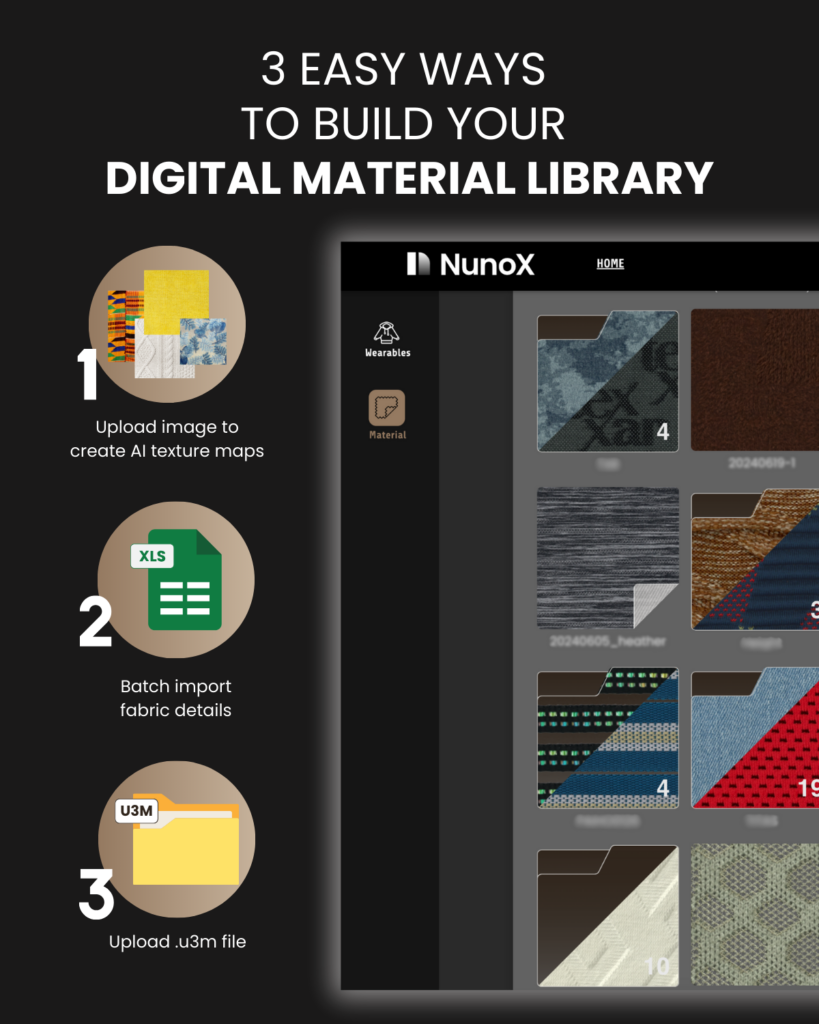
1. Create your own searchable digital material library
Building a digital fabric library offers easy organization and quick access to all your material assets. With a searchable database, you can find fabric details and inventory instantly without needing the physical material on hand.
2. Save on physical sampling production and shipping cost
Digitizing fabrics reduces the number of sampling rounds, saving production and shipping costs. Minimize the environmental impact of wasted textiles and reduce transportation carbon emissions by going digital first. The cost savings can be reallocated to other areas, like upskilling the team’s digital software capabilities.
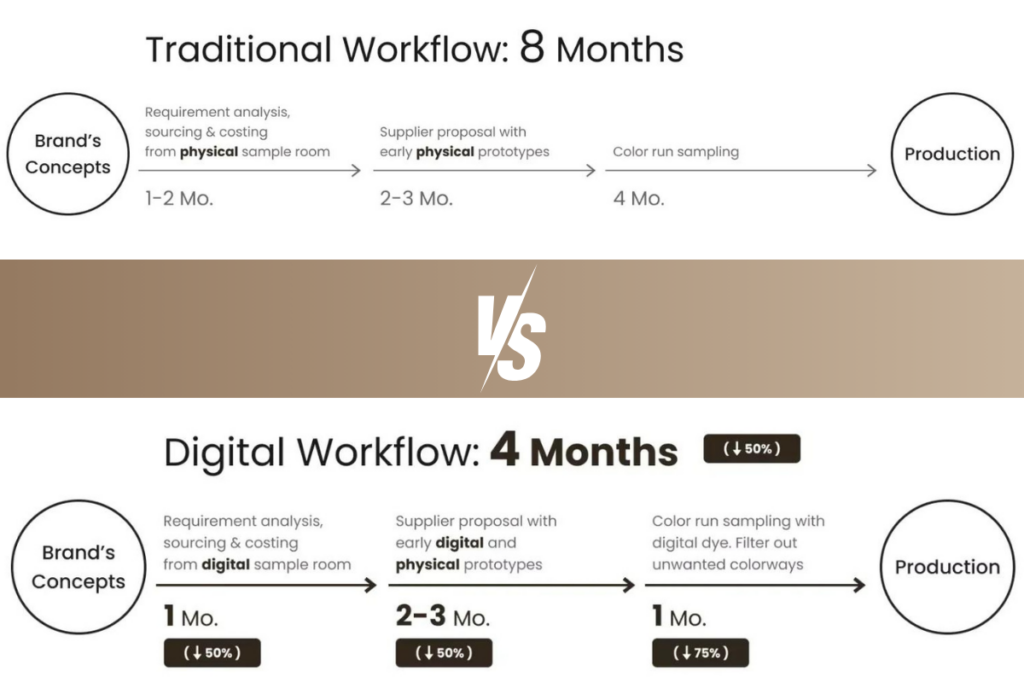
3. Accelerate product development cycle
Digital fabrics enable rapid prototyping and iterative design, shortening the product creation cycle. The flexibility provided by digital prototypes fosters creative freedom, allowing for quick adjustments and more innovative, diverse collections. Digital prototypes reduce the number of sampling rounds and long wait times from product concept to production.
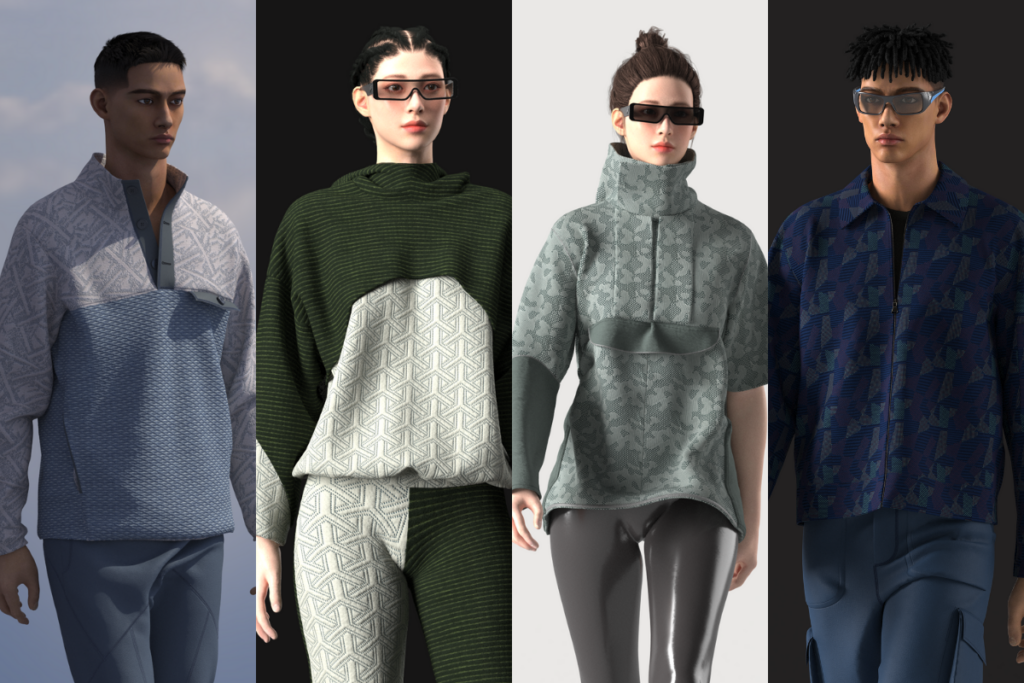
4. Create high-quality visual content for marketing and sales
Digital materials make it easier to develop realistic 3D renderings for product images. No more costly in-person photoshoots. These high-quality visuals can be used across e-commerce platforms, social media, online advertisements, and other promotional content to showcase different product features.

5. Enhance collaboration across teams
Digital fabrics significantly improve collaboration among teams, regardless of their location. Designers, manufacturers, and clients can share and review digital assets instantly, enabling real-time feedback. Speed up overall project timelines with easy communication for a quick approval process.
Material Digitization is the Future of Textiles
Sustainability and innovation go hand-in-hand to solve the fashion industry’s pressing challenges. Integrating fabric scanners to create digital materials offers a potential solution to many of the industry’s pressing challenges, from reducing waste to accelerating design processes.
By digitizing physical fabrics, designers and manufacturers can explore new creative possibilities, streamline production, and contribute to a more sustainable future. As the demand for efficiency and eco-friendly practices grows, embracing these digital tools is necessary for staying competitive in the evolving market. Explore the latest fabric scanning technologies, and begin building your digital assets to be ready for the technological future of fashion.
Read more: 3D Fabric Scanning: The New Frontier in Textile Digitization Over 2D Photos?
